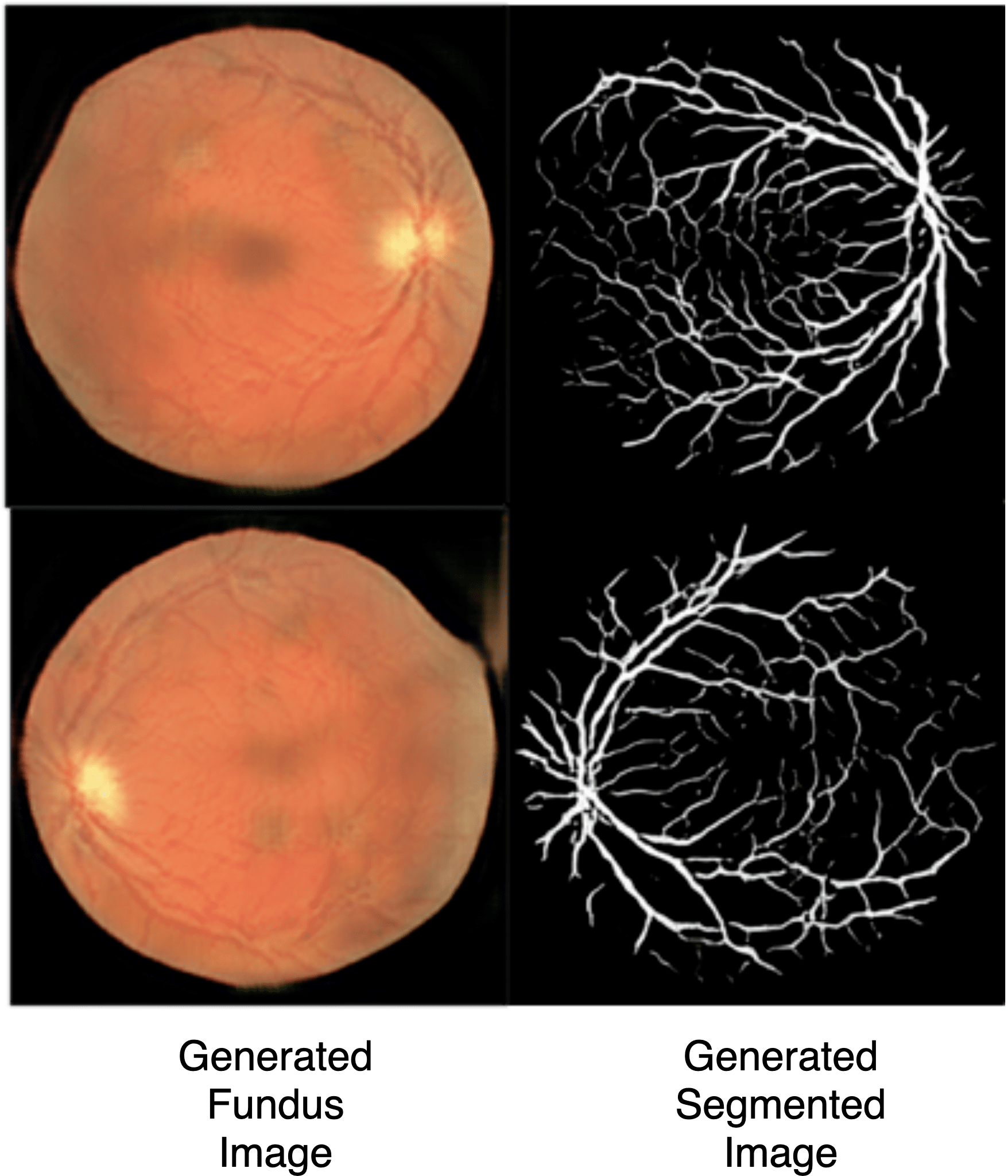
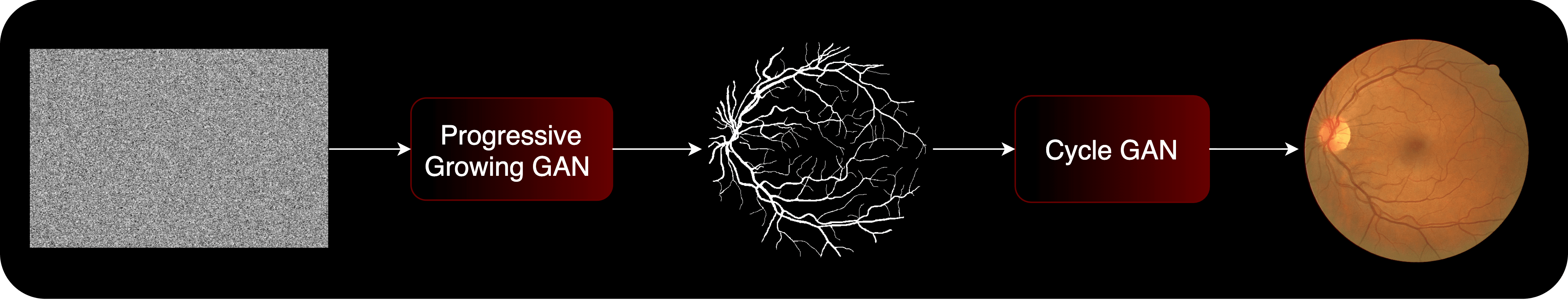
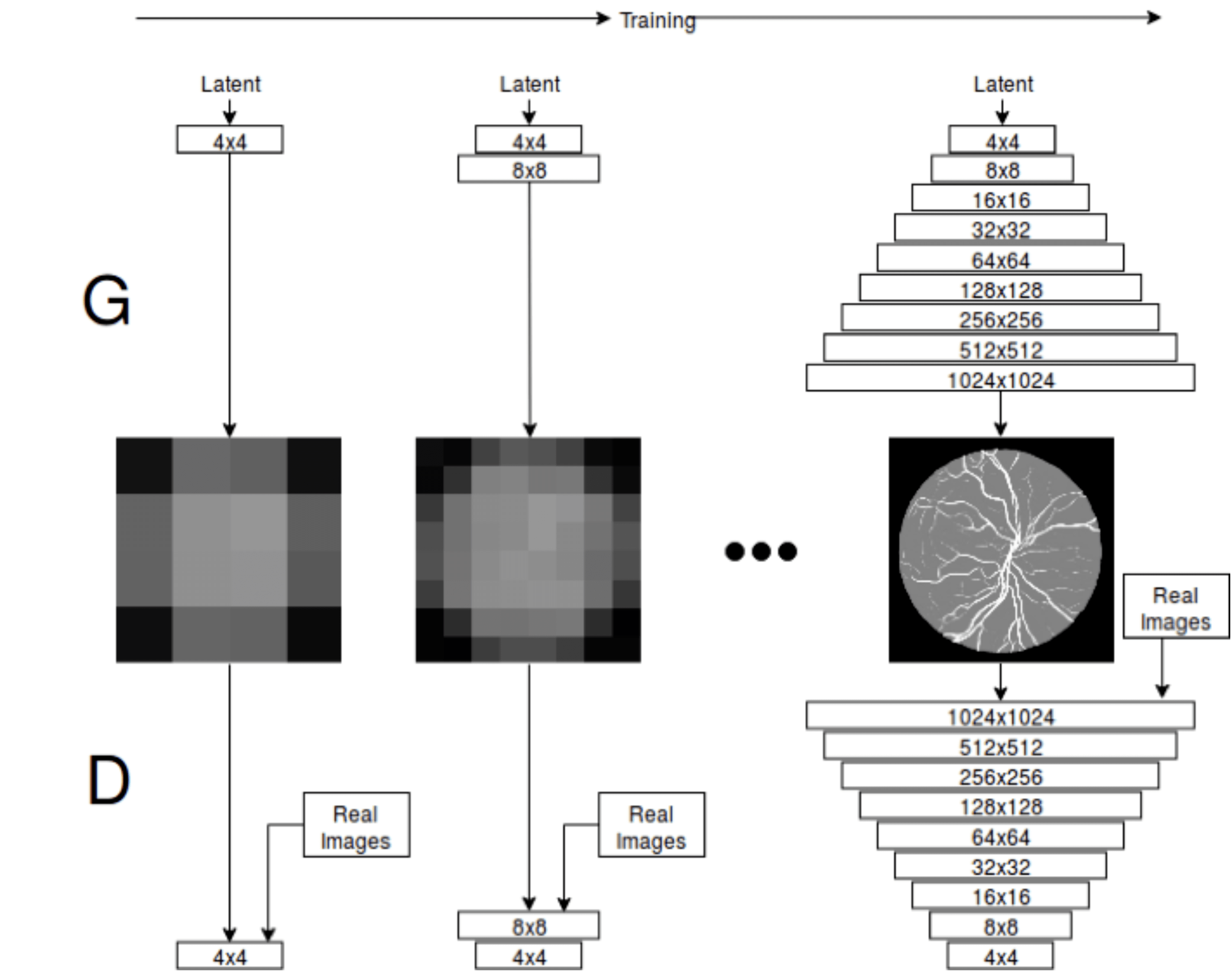
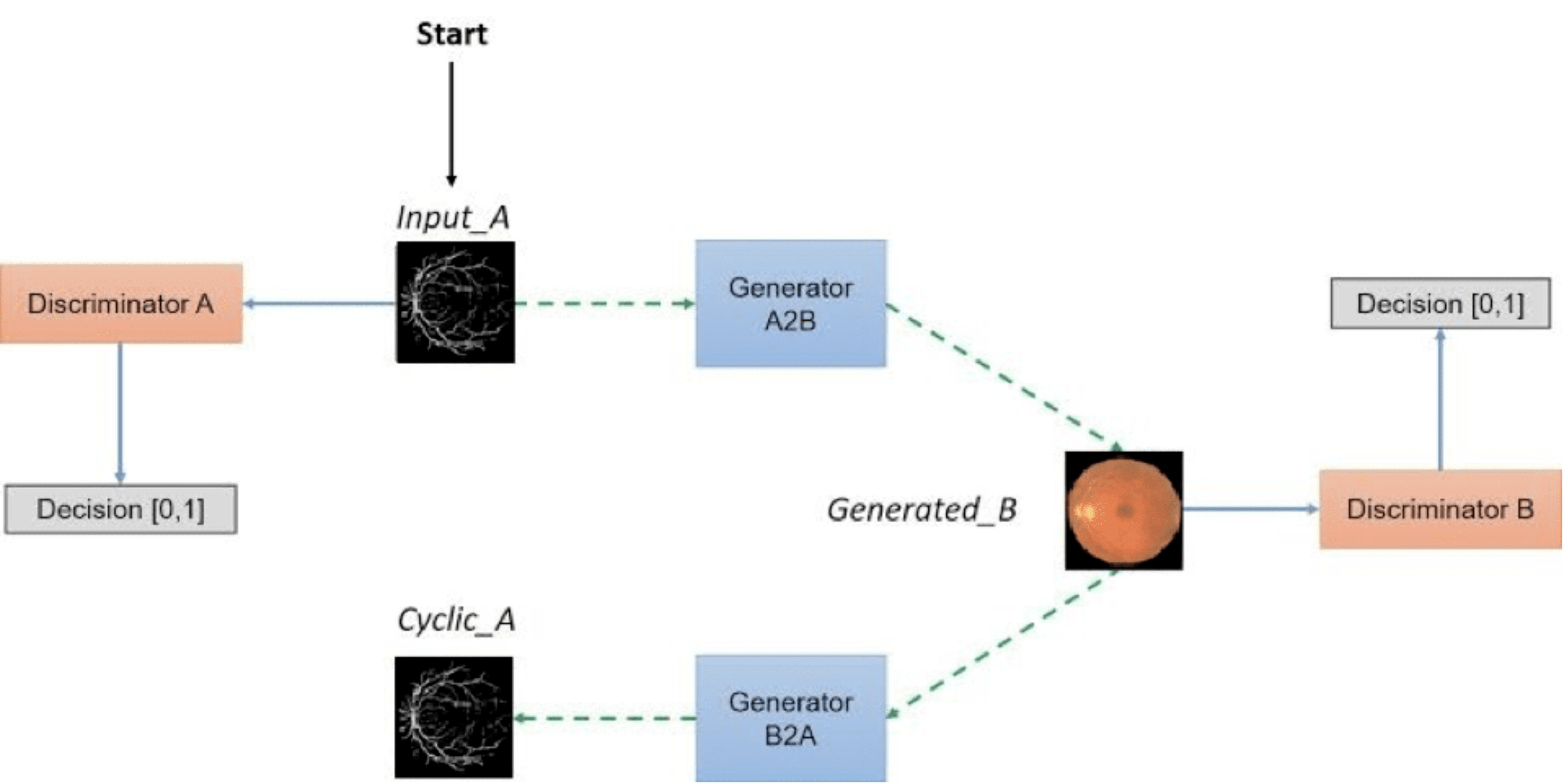
Medical imaging data is scarce, expensive, and fraught with legal concerns regarding patient privacy. However, adequate training of deep learning architectures relies on a broad set of labelled data. This is critical in medical imaging, where it is difficult and expensive to obtain labelled data. In this project, we propose a novel, fully unsupervised two-step pipeline for synthesizing high-quality retinal images, along with the corresponding segmented vessel structure. In the first step, a Progressive Growing GAN is trained to generate semantic label maps of the blood vessel structure. Second, the generated label maps are translated to realistic retinal images using an unpaired image-to-image translation approach. Training the network on a handful of training images, we were able to generate high-resolution images that can be used to enlarge small available datasets.
Retinal Image Generation and Segmentation using Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract
Technologies:
- - Python
- - Pytorch
- - Numpy
- - Matplotlib
Dataset
DRIVE dataset – The DRIVE dataset includes 40 retinal–fundus images of size 584 *565*3. The images have been collected by a screening program for diabetic retinopathy in the Netherlands. Among the 40 photographs, 33 show no diabetic retinopathy, while 7 show mild early diabetic retinopathy. Segmentation ground–truth is provided both for training and test sets.
Pipeline
Results